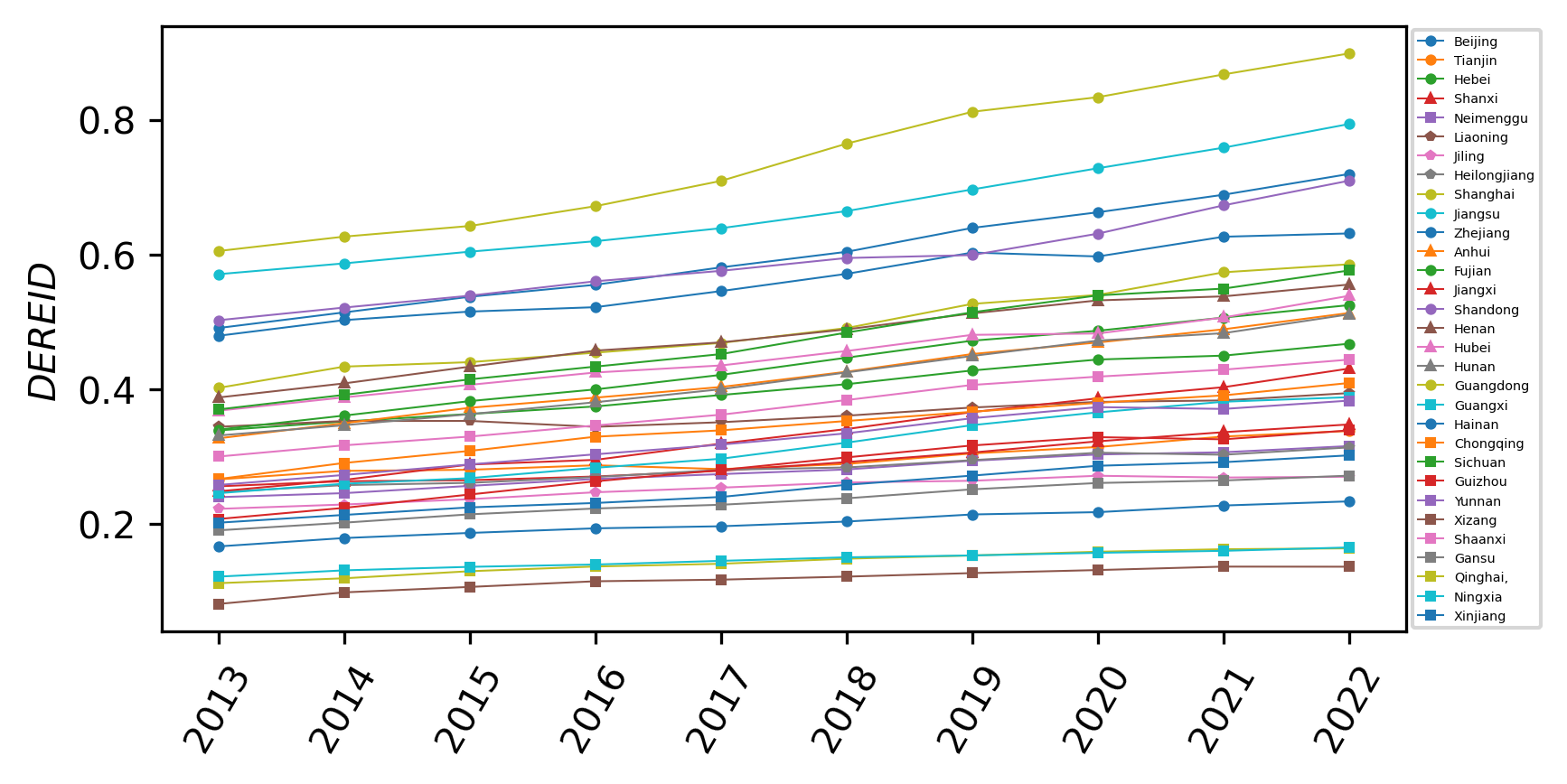
Herd behavior refers to the tendency of individuals to imitate others' behaviors or opinions rather than engaging in independent thinking when facing uncertainty or ambiguity. This phenomenon is extremely common in the fields of finance and economics. In view of the severe volatility exhibited by the real estate market in the post-pandemic period, this study focuses on the real estate market—particularly the herd behavior in China’s real estate market, which has experienced drastic fluctuations in recent years. The aim is to empirically verify the existence of such herd behavior and explore its influencing factors through empirical analysis. A Spatial Autoregressive Model (SAR) is employed, with variables including housing prices, personal disposable income, and one-year personal housing loan interest rates incorporated for modeling. The results indicate that significant herd behavior exists in the real estate market, and various factors exert influences on it to varying degrees. This study provides empirical evidence for understanding the operational mechanism of the real estate market and formulating reasonable policies.
Research Article
Open Access